The study of reaction diagrams is crucial in understanding the chemical reactions that occur in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and physics. One of the key aspects of reaction diagrams is the formation of bonds between atoms or molecules. In this article, we will delve into the world of reaction diagrams and explore the bonds formed in these diagrams.
Understanding reaction diagrams is essential in predicting the outcome of chemical reactions. These diagrams provide a visual representation of the reactants, products, and intermediates involved in a reaction. By analyzing reaction diagrams, chemists can identify the bonds formed between atoms or molecules, which is critical in understanding the reaction mechanism.
What are Reaction Diagrams?

Reaction diagrams, also known as reaction schemes or reaction pathways, are graphical representations of chemical reactions. These diagrams illustrate the reactants, products, and intermediates involved in a reaction, as well as the bonds formed between them. Reaction diagrams are typically drawn using arrows to indicate the direction of the reaction and the bonds formed between atoms or molecules.
Types of Bonds Formed in Reaction Diagrams

There are several types of bonds that can be formed in reaction diagrams, including:
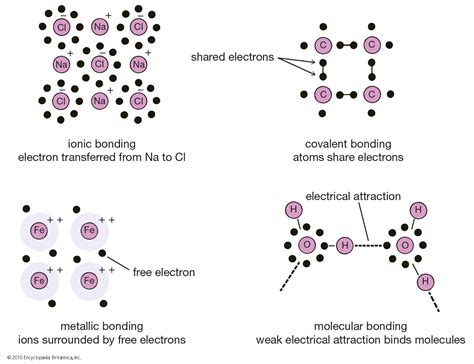
- Covalent bonds: These bonds are formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. Covalent bonds are typically represented by a line between the atoms involved in the bond.
- Ionic bonds: These bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions. Ionic bonds are typically represented by an arrow pointing from the positively charged ion to the negatively charged ion.
- Hydrogen bonds: These bonds are formed when a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen, interacts with another electronegative atom. Hydrogen bonds are typically represented by a dotted line between the atoms involved in the bond.
- Pi bonds: These bonds are formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons in a parallel orientation. Pi bonds are typically represented by a parallel line between the atoms involved in the bond.
How to Identify Bonds in Reaction Diagrams

Identifying bonds in reaction diagrams can be a challenging task, especially for those who are new to chemistry. Here are some tips to help you identify bonds in reaction diagrams:
- Look for lines between atoms: Lines between atoms typically indicate the formation of covalent bonds.
- Look for arrows between atoms: Arrows between atoms typically indicate the formation of ionic bonds.
- Look for dotted lines between atoms: Dotted lines between atoms typically indicate the formation of hydrogen bonds.
- Look for parallel lines between atoms: Parallel lines between atoms typically indicate the formation of pi bonds.
Importance of Bonds in Reaction Diagrams

Bonds play a crucial role in reaction diagrams, as they help to predict the outcome of chemical reactions. By identifying the bonds formed between atoms or molecules, chemists can:
- Predict the products of a reaction: By identifying the bonds formed between reactants, chemists can predict the products of a reaction.
- Understand the reaction mechanism: By identifying the bonds formed between reactants and intermediates, chemists can understand the reaction mechanism.
- Design new reactions: By identifying the bonds formed between reactants, chemists can design new reactions that form specific products.
Real-World Applications of Bonds in Reaction Diagrams

Bonds in reaction diagrams have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Bonds in reaction diagrams are used to design new pharmaceuticals that target specific diseases.
- Materials science: Bonds in reaction diagrams are used to design new materials with specific properties.
- Environmental science: Bonds in reaction diagrams are used to understand and predict the fate of pollutants in the environment.
In conclusion, bonds play a crucial role in reaction diagrams, and understanding these bonds is essential in predicting the outcome of chemical reactions. By identifying the bonds formed between atoms or molecules, chemists can predict the products of a reaction, understand the reaction mechanism, and design new reactions.
We encourage you to share your thoughts on the importance of bonds in reaction diagrams. How do you think bonds in reaction diagrams can be used to solve real-world problems? Share your comments below!
What is a reaction diagram?
+A reaction diagram is a graphical representation of a chemical reaction, illustrating the reactants, products, and intermediates involved in the reaction.
What types of bonds can be formed in reaction diagrams?
+Covalent bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and pi bonds can be formed in reaction diagrams.
Why are bonds important in reaction diagrams?
+Bonds are important in reaction diagrams because they help predict the outcome of chemical reactions, understand the reaction mechanism, and design new reactions.