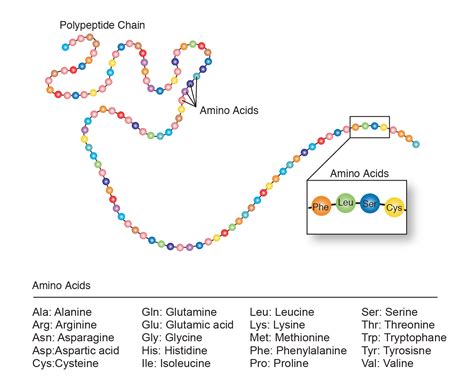
Proteins are the building blocks of life, and their unique structures and functions are determined by the sequence of amino acids that make them up. Amino acids are the individual units that are linked together to form proteins, and the specific sequence of these amino acids determines the final shape and function of the protein. Understanding how proteins form through amino acid sequences is crucial for understanding the intricacies of life itself.
The process of protein formation, also known as protein synthesis, is a complex and highly regulated process that involves multiple steps and cellular components. It begins with the transcription of DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA), which carries the genetic information necessary for protein synthesis. The mRNA then travels out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm, where it is translated into a sequence of amino acids.

Understanding Amino Acids
Amino acids are the individual units that make up proteins. There are 20 different amino acids that are commonly found in proteins, each with its own unique structure and properties. Amino acids are composed of a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain that varies depending on the specific amino acid.
Amino acids are linked together through peptide bonds, which form between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another. This creates a long chain of amino acids, known as a polypeptide chain, which folds into a specific three-dimensional structure to form a protein.
Amino Acid Properties
Amino acids have several important properties that determine their role in protein structure and function. These properties include:
- Charge: Amino acids can be positively charged, negatively charged, or neutral, which affects their interactions with other amino acids and molecules.
- Hydrophobicity: Amino acids can be hydrophobic (water-repelling) or hydrophilic (water-attracting), which affects their interactions with water and other molecules.
- Size: Amino acids vary in size, which affects their ability to fit into specific spaces and interact with other molecules.
- Polarity: Amino acids can be polar or nonpolar, which affects their interactions with other molecules and their ability to form hydrogen bonds.
These properties determine the specific roles that amino acids play in protein structure and function, and understanding them is essential for understanding how proteins form and function.
The Process of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins from amino acids. It involves multiple steps, including transcription, translation, and post-translational modification.

Transcription
Transcription is the first step in protein synthesis, in which the genetic information in DNA is copied into a complementary RNA molecule. This process is initiated when an enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to the DNA and begins to unwind the double helix. The RNA polymerase then reads the template strand of DNA and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules.
Translation
Translation is the second step in protein synthesis, in which the mRNA molecule is translated into a sequence of amino acids. This process occurs on structures called ribosomes, which are composed of two subunits that come together to form a complex. The ribosome reads the sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA and matches the incoming amino acids to the sequence.
Post-Translational Modification
Post-translational modification is the final step in protein synthesis, in which the newly synthesized protein is modified to its final form. This can involve the addition of carbohydrates, lipids, or phosphate groups, as well as the formation of disulfide bonds or other covalent modifications.
Protein Structure and Function
Proteins have a wide range of structures and functions, and understanding how they form and function is crucial for understanding the intricacies of life. Proteins can be broadly classified into several categories, including:
- Enzymes: Proteins that catalyze chemical reactions.
- Hormones: Proteins that act as signaling molecules.
- Transport proteins: Proteins that transport molecules across cell membranes.
- Structural proteins: Proteins that provide structural support and shape to cells and tissues.

Primary Structure
The primary structure of a protein refers to the sequence of amino acids that make it up. This sequence is determined by the genetic code, and it determines the final shape and function of the protein.
Secondary Structure
The secondary structure of a protein refers to the local arrangements of amino acids, such as alpha helices and beta sheets. These structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonds and other interactions between amino acids.
Tertiary Structure
The tertiary structure of a protein refers to the overall three-dimensional shape of the protein. This structure is determined by the interactions between amino acids and is stabilized by disulfide bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and other forces.
Quaternary Structure
The quaternary structure of a protein refers to the arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains in a protein. This structure is determined by the interactions between amino acids and is stabilized by disulfide bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and other forces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, proteins form through the sequence of amino acids that make them up. Understanding how proteins form and function is crucial for understanding the intricacies of life itself. The process of protein synthesis involves multiple steps, including transcription, translation, and post-translational modification. The structure and function of proteins are determined by their amino acid sequence, and understanding these structures and functions is essential for understanding the complexities of life.
What are amino acids?
+Amino acids are the individual units that make up proteins. There are 20 different amino acids that are commonly found in proteins, each with its own unique structure and properties.
How do proteins form?
+Proteins form through the sequence of amino acids that make them up. The process of protein synthesis involves multiple steps, including transcription, translation, and post-translational modification.
What determines the structure and function of proteins?
+The structure and function of proteins are determined by their amino acid sequence. The sequence of amino acids determines the final shape and function of the protein, and understanding these structures and functions is essential for understanding the complexities of life.