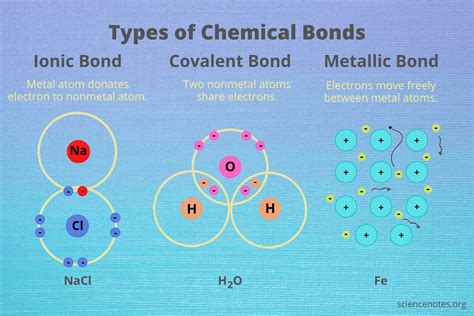
Ionic bonds are a crucial aspect of chemistry, playing a vital role in the formation of various compounds. These bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions holds them together, forming a strong and stable chemical bond. In this article, we will delve into the three types of elements that form ionic bonds.
What are Ionic Bonds?

Ionic bonds are a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. This transfer of electrons results in the formation of ions with opposite charges, which are then attracted to each other due to electrostatic forces. Ionic bonds are typically formed between metals and nonmetals, resulting in the formation of ionic compounds.
Type 1: Metals

Metals are one of the primary types of elements that form ionic bonds. Metals are typically found on the left side of the periodic table and are known for their ability to lose electrons easily. When a metal atom loses one or more electrons, it forms a positively charged ion, known as a cation. This cation is then attracted to a negatively charged ion, known as an anion, which is typically formed when a nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons.
Examples of metals that form ionic bonds include sodium (Na), calcium (Ca), and magnesium (Mg). These metals are commonly found in ionic compounds such as sodium chloride (NaCl), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and magnesium oxide (MgO).
Properties of Metals that Form Ionic Bonds
- Highly electropositive
- Tend to lose electrons easily
- Form positively charged ions (cations)
- Typically found on the left side of the periodic table
Type 2: Nonmetals

Nonmetals are another type of element that forms ionic bonds. Nonmetals are typically found on the right side of the periodic table and are known for their ability to gain electrons easily. When a nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons, it forms a negatively charged ion, known as an anion. This anion is then attracted to a positively charged ion, known as a cation, which is typically formed when a metal atom loses one or more electrons.
Examples of nonmetals that form ionic bonds include oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and chlorine (Cl). These nonmetals are commonly found in ionic compounds such as sodium chloride (NaCl), magnesium oxide (MgO), and calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
Properties of Nonmetals that Form Ionic Bonds
- Highly electronegative
- Tend to gain electrons easily
- Form negatively charged ions (anions)
- Typically found on the right side of the periodic table
Type 3: Metalloids

Metalloids are a type of element that exhibits some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. Metalloids are typically found on the border between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table and are known for their ability to form ions with both positive and negative charges. When a metalloid atom loses one or more electrons, it forms a positively charged ion, while gaining one or more electrons results in the formation of a negatively charged ion.
Examples of metalloids that form ionic bonds include boron (B), silicon (Si), and germanium (Ge). These metalloids are commonly found in ionic compounds such as boron carbide (B4C), silicon dioxide (SiO2), and germanium oxide (GeO2).
Properties of Metalloids that Form Ionic Bonds
- Exhibit some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals
- Can form ions with both positive and negative charges
- Typically found on the border between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table
In conclusion, ionic bonds are a crucial aspect of chemistry, and understanding the types of elements that form these bonds is essential for understanding various chemical compounds. Metals, nonmetals, and metalloids are the three types of elements that form ionic bonds, each with unique properties that enable them to form ions with opposite charges. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of ionic bonds and the elements that form them.
What is an ionic bond?
+An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
What are the three types of elements that form ionic bonds?
+The three types of elements that form ionic bonds are metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
What is the difference between a metal and a nonmetal?
+A metal is an element that tends to lose electrons easily, while a nonmetal is an element that tends to gain electrons easily.