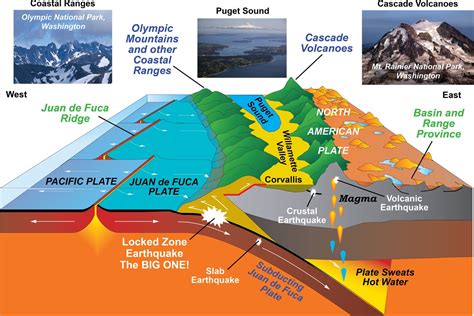
The Earth's lithosphere is a dynamic and constantly evolving system, shaped by the forces of plate tectonics. One of the most fascinating and awe-inspiring consequences of these forces is the creation of mountain ranges and volcanic landforms at convergent boundaries. In this article, we will delve into the world of convergent boundaries, exploring the processes that shape our planet's surface and create some of its most breathtaking landscapes.
Convergent boundaries are areas where two or more tectonic plates are moving towards each other, resulting in the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes. This type of boundary is characterized by the subduction of one plate beneath another, a process known as subduction. As the overlying plate is subjected to increasing heat and pressure, it begins to melt, producing magma that rises to the surface, creating volcanoes. The resulting landscape is a testament to the incredible forces that shape our planet.
The Process of Mountain Building at Convergent Boundaries

At convergent boundaries, the process of mountain building is a complex and multifaceted one. As the two plates converge, the Earth's crust is compressed and thickened, resulting in the formation of a mountain range. This process can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including faulting, folding, and volcanic activity. The resulting mountains can be some of the most spectacular and awe-inspiring landscapes on the planet, with towering peaks, deep valleys, and glaciers.
One of the most iconic examples of mountain building at a convergent boundary is the Himalayan mountain range. Formed as a result of the collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates, the Himalayas are the highest mountain range on Earth, with peaks reaching elevations of over 8,000 meters. The process of mountain building in this region is ongoing, with the Indian plate continuing to move northwards into the Eurasian plate, resulting in the formation of new mountains and the uplift of existing ones.
Types of Convergent Boundaries
There are three main types of convergent boundaries: oceanic-continental, oceanic-oceanic, and continental-continental. Each of these types of boundaries has its own unique characteristics and resulting landforms.
- Oceanic-continental convergent boundaries occur where an oceanic plate is being subducted beneath a continental plate. This type of boundary is characterized by the formation of a volcanic arc, with volcanoes forming as a result of the melting of the overlying plate.
- Oceanic-oceanic convergent boundaries occur where two oceanic plates are converging. This type of boundary is characterized by the formation of a deep-sea trench, with the subducting plate being forced beneath the overriding plate.
- Continental-continental convergent boundaries occur where two continental plates are converging. This type of boundary is characterized by the formation of a mountain range, with the two plates being pushed upwards to form a zone of deformation.
Volcanic Landforms at Convergent Boundaries

Volcanic landforms are a common feature of convergent boundaries, resulting from the melting of the overlying plate as it is subjected to increasing heat and pressure. The resulting magma rises to the surface, producing volcanoes that can be highly explosive and destructive. Some of the most notable examples of volcanic landforms at convergent boundaries include:
- The Ring of Fire: A zone of intense volcanic and seismic activity that encircles the Pacific Ocean, resulting from the subduction of several oceanic plates beneath the North American and Eurasian plates.
- The Andes mountain range: A chain of volcanoes that stretches along the western edge of South America, resulting from the subduction of the Nazca plate beneath the South American plate.
- Mount Fuji: A highly iconic and active volcano in Japan, resulting from the subduction of the Pacific plate beneath the North American plate.
Examples of Convergent Boundaries
There are many examples of convergent boundaries around the world, each with its own unique characteristics and resulting landforms. Some of the most notable examples include:
- The Himalayan mountain range: Formed as a result of the collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates.
- The Andes mountain range: Formed as a result of the subduction of the Nazca plate beneath the South American plate.
- The Japan Trench: A deep-sea trench formed as a result of the subduction of the Pacific plate beneath the North American plate.
Earthquakes at Convergent Boundaries

Earthquakes are a common feature of convergent boundaries, resulting from the movement of the tectonic plates. As the plates converge, they can become stuck, resulting in a buildup of stress. When this stress is released, it can result in a powerful earthquake. Some of the most notable examples of earthquakes at convergent boundaries include:
- The 2011 Tohoku earthquake: A magnitude 9.0 earthquake that occurred off the coast of Japan, resulting from the subduction of the Pacific plate beneath the North American plate.
- The 2004 Sumatran earthquake: A magnitude 9.1 earthquake that occurred off the coast of Indonesia, resulting from the subduction of the Indian plate beneath the Eurasian plate.
Conclusion
Convergent boundaries are areas of incredible geological activity, resulting in the formation of mountain ranges and volcanic landforms. Through the process of subduction, the overlying plate is subjected to increasing heat and pressure, resulting in the melting of the plate and the formation of magma. This magma rises to the surface, producing volcanoes that can be highly explosive and destructive. Earthquakes are also a common feature of convergent boundaries, resulting from the movement of the tectonic plates.
As we continue to explore and study the Earth's lithosphere, we are constantly reminded of the incredible forces that shape our planet. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the explosive volcanoes of the Ring of Fire, convergent boundaries are a testament to the dynamic and constantly evolving nature of our planet.
We hope you found this article informative and engaging. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. We would love to hear from you!
What is a convergent boundary?
+A convergent boundary is an area where two or more tectonic plates are moving towards each other, resulting in the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
What is subduction?
+Subduction is the process by which one tectonic plate is forced beneath another, resulting in the melting of the overlying plate and the formation of magma.
What are some examples of convergent boundaries?
+Some examples of convergent boundaries include the Himalayan mountain range, the Andes mountain range, and the Japan Trench.