Covalent bonds are a fundamental aspect of chemistry, and understanding the elements that form these bonds is crucial for grasping the basics of chemistry. In this article, we will delve into the world of covalent bonds, exploring the elements that form these bonds, the types of covalent bonds, and the factors that influence their formation.
What are Covalent Bonds?

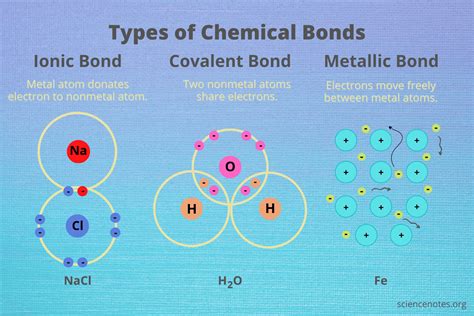
Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bond that forms between two or more atoms that share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons leads to the formation of a molecule, where the atoms are held together by the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged nuclei and the negatively charged electrons. Covalent bonds are typically found in molecules, where the atoms are connected by a shared pair of electrons.
Types of Covalent Bonds
There are several types of covalent bonds, including:
- Single covalent bonds: These bonds involve the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms.
- Double covalent bonds: These bonds involve the sharing of two pairs of electrons between two atoms.
- Triple covalent bonds: These bonds involve the sharing of three pairs of electrons between two atoms.
Elements That Form Covalent Bonds

Covalent bonds can form between a wide range of elements, including nonmetals, metalloids, and some metals. Some of the most common elements that form covalent bonds include:
- Hydrogen (H)
- Carbon (C)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Sulfur (S)
- Phosphorus (P)
These elements tend to form covalent bonds with each other, as well as with other elements, to form a wide range of molecules.
Factors That Influence Covalent Bond Formation
Several factors can influence the formation of covalent bonds, including:
- Electronegativity: The difference in electronegativity between two atoms can affect the formation of a covalent bond. Atoms with high electronegativity values tend to attract electrons more strongly, making it more difficult for a covalent bond to form.
- Atomic size: The size of the atoms involved in the bond can also affect the formation of a covalent bond. Smaller atoms tend to form stronger covalent bonds due to the closer proximity of the electrons.
- Valence electrons: The number of valence electrons available for bonding can also influence the formation of a covalent bond. Atoms with more valence electrons tend to form more covalent bonds.
Examples of Covalent Bonds in Molecules

Covalent bonds are found in a wide range of molecules, including:
- Water (H2O)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Methane (CH4)
- Ethanol (C2H5OH)
These molecules are all composed of atoms that are connected by covalent bonds, which hold the atoms together and give the molecule its shape and properties.
Importance of Covalent Bonds in Chemistry
Covalent bonds play a crucial role in chemistry, as they are responsible for holding molecules together and giving them their unique properties. Understanding covalent bonds is essential for understanding many chemical processes, including:
- Chemical reactions: Covalent bonds are involved in many chemical reactions, including combustion reactions, synthesis reactions, and decomposition reactions.
- Molecular structure: Covalent bonds determine the shape and structure of molecules, which is essential for understanding their properties and behavior.
- Biological processes: Covalent bonds are involved in many biological processes, including the formation of DNA, proteins, and other biomolecules.
Conclusion: Covalent Bonds and Their Importance in Chemistry

In conclusion, covalent bonds are a fundamental aspect of chemistry, and understanding the elements that form these bonds is crucial for grasping the basics of chemistry. Covalent bonds are found in a wide range of molecules, and they play a crucial role in many chemical processes. By understanding covalent bonds, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the chemical world and the many processes that occur within it.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions about covalent bonds in the comments section below. If you have any specific questions or topics you would like to discuss, please don't hesitate to ask.
What is the difference between a covalent bond and an ionic bond?
+A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two or more atoms that share one or more pairs of electrons. An ionic bond, on the other hand, is a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms that have a large difference in electronegativity, resulting in the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
What are some common examples of molecules that contain covalent bonds?
+Some common examples of molecules that contain covalent bonds include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), ammonia (NH3), methane (CH4), and ethanol (C2H5OH).
What is the role of electronegativity in the formation of covalent bonds?
+Electronegativity plays a crucial role in the formation of covalent bonds. Atoms with high electronegativity values tend to attract electrons more strongly, making it more difficult for a covalent bond to form.