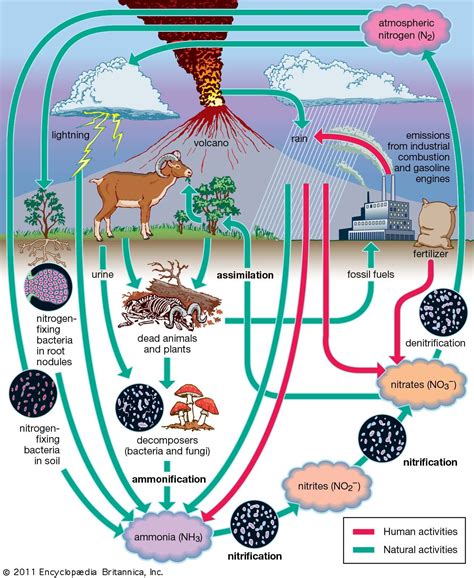
Nitrogen is an essential element for life on Earth, and it's a critical component of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Despite its abundance in the atmosphere, nitrogen is not readily available for use by most living organisms. This is because atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is a stable molecule that requires a significant amount of energy to break apart and convert into a usable form. Fortunately, certain microorganisms, such as bacteria, have evolved the ability to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by other living organisms. This process is known as nitrogen fixation.

Nitrogen fixation is a critical process that supports the entire food chain. Without it, plants would not be able to obtain the nitrogen they need to grow, and herbivores would not have access to the nitrogen-rich plants they need to survive. The process of nitrogen fixation is complex and involves a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that require a significant amount of energy.
How Nitrogen Fixation Works
Nitrogen fixation is carried out by specialized bacteria that contain the enzyme nitrogenase. Nitrogenase is a complex enzyme that consists of two proteins: dinitrogenase and dinitrogenase reductase. These proteins work together to catalyze the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia (NH3).

The process of nitrogen fixation involves several steps:
- Nitrogenase activation: The nitrogenase enzyme is activated by the binding of ATP and a reducing agent, such as ferredoxin.
- Nitrogen binding: The activated nitrogenase enzyme binds to atmospheric nitrogen, forming a complex.
- Reduction: The nitrogen complex is reduced by the transfer of electrons from the reducing agent.
- Ammonia formation: The reduced nitrogen complex is converted into ammonia (NH3).
Types of Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria
There are several types of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, including:
- Rhizobia: These bacteria live in symbiosis with legume plants, such as beans and peas. They infect the plant's roots and form nodules, where they fix nitrogen.
- Frankia: These bacteria live in symbiosis with actinorhizal plants, such as alder and bayberry. They also form nodules on the plant's roots, where they fix nitrogen.
- Azotobacter: These bacteria are free-living and can fix nitrogen in the soil.
- Cyanobacteria: These bacteria are photosynthetic and can fix nitrogen in aquatic environments.
Importance of Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is essential for life on Earth. Without it, plants would not be able to obtain the nitrogen they need to grow, and herbivores would not have access to the nitrogen-rich plants they need to survive. Nitrogen fixation also supports the entire food chain, from plants to herbivores to carnivores.

In addition to its importance in supporting the food chain, nitrogen fixation also plays a critical role in maintaining soil fertility. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria help to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by plants, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Challenges and Opportunities
While nitrogen fixation is an essential process, it also presents several challenges and opportunities. For example:
- Climate change: Climate change is affecting the distribution and abundance of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which could have significant impacts on ecosystems.
- Soil degradation: Soil degradation is reducing the availability of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which could have significant impacts on plant growth and soil fertility.
- Sustainable agriculture: Nitrogen fixation could play a critical role in sustainable agriculture by reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and promoting soil health.

In conclusion, nitrogen fixation is a critical process that supports the entire food chain. It's essential for plant growth, soil fertility, and maintaining ecosystem health. While there are challenges and opportunities associated with nitrogen fixation, it's clear that this process will continue to play a vital role in supporting life on Earth.
Get Involved
If you're interested in learning more about nitrogen fixation or getting involved in sustainable agriculture, there are several ways to do so:
- Volunteer: Volunteer with organizations that promote sustainable agriculture and soil health.
- Learn more: Learn more about nitrogen fixation and its importance in supporting ecosystems.
- Support sustainable agriculture: Support sustainable agriculture by choosing to buy from local farmers who use nitrogen-fixing bacteria.

FAQ Section:
What is nitrogen fixation?
+Nitrogen fixation is the process by which certain microorganisms, such as bacteria, convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by other living organisms.
Why is nitrogen fixation important?
+Nitrogen fixation is essential for life on Earth, as it supports the entire food chain and maintains soil fertility.
What are some challenges associated with nitrogen fixation?
+Some challenges associated with nitrogen fixation include climate change, soil degradation, and the need for sustainable agriculture practices.