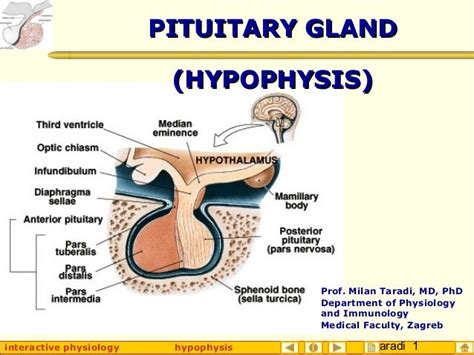
The pituitary gland is a small endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, playing a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, and reproductive processes. The combining form "hypophyseal" is derived from the Greek words "hypo," meaning "under," and "physis," meaning "growth," which refers to the gland's location and function. Understanding the roots and meaning of the term "hypophyseal" can provide valuable insights into the pituitary gland's significance and its role in maintaining overall health.

The term "hypophyseal" is used to describe the pituitary gland's functions, disorders, and related medical procedures. For instance, hypophyseal hypoplasia refers to the underdevelopment of the pituitary gland, while hypophyseal stalk compression is a condition where the pituitary stalk is compressed, disrupting hormone production. Understanding the combining form "hypophyseal" can help medical professionals and patients communicate more effectively about pituitary gland-related conditions.
Functions of the Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is often referred to as the "master gland" because it regulates the function of other endocrine glands, including the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and gonads. The pituitary gland produces several hormones that stimulate or inhibit the production of hormones in other glands, maintaining a delicate balance of hormone levels in the body.

Some of the key functions of the pituitary gland include:
- Regulating growth and development during childhood and adolescence
- Controlling metabolism and energy production
- Regulating reproductive processes, including fertility and menstruation
- Maintaining electrolyte balance and blood pressure
- Regulating the body's response to stress
Disorders of the Pituitary Gland
Pituitary gland disorders can occur due to various factors, including genetic mutations, tumors, and traumatic injuries. Some common disorders of the pituitary gland include:
- Hypopituitarism: a condition where the pituitary gland does not produce enough hormones
- Hyperpituitarism: a condition where the pituitary gland produces too many hormones
- Pituitary tumors: benign or malignant growths that can compress the pituitary gland or surrounding tissues
- Pituitary stalk compression: a condition where the pituitary stalk is compressed, disrupting hormone production

Symptoms of pituitary gland disorders can vary depending on the specific condition and the hormones affected. Common symptoms include:
- Growth and development problems in children
- Fatigue, weakness, and muscle wasting
- Changes in appetite and metabolism
- Reproductive problems, including infertility and irregular menstruation
- Headaches and vision problems
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pituitary Gland Disorders
Diagnosing pituitary gland disorders typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Treatment options depend on the specific condition and may include:
- Hormone replacement therapy to replace deficient hormones
- Surgery to remove tumors or compressive lesions
- Radiation therapy to shrink tumors
- Medications to regulate hormone production

In some cases, treatment may involve a combination of these options. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs and goals of each individual.
Prevention and Early Detection
While some pituitary gland disorders are inherited or caused by genetic mutations, others can be prevented or detected early through lifestyle modifications and regular medical check-ups.

Some ways to promote pituitary gland health include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight and diet
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga
- Avoiding exposure to toxins and radiation
- Getting regular medical check-ups and screenings
Early detection of pituitary gland disorders can significantly improve treatment outcomes and quality of life. If you are experiencing symptoms or have concerns about your pituitary gland health, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and care.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The pituitary gland plays a vital role in maintaining overall health, and understanding the combining form "hypophyseal" can provide valuable insights into its functions and disorders. By recognizing the importance of pituitary gland health and taking steps to promote prevention and early detection, individuals can reduce their risk of developing related disorders and improve their overall well-being.

As research continues to advance our understanding of the pituitary gland and its disorders, new treatment options and prevention strategies are likely to emerge. By staying informed and engaged, individuals can take an active role in promoting their pituitary gland health and overall well-being.
What is the function of the pituitary gland?
+The pituitary gland regulates the function of other endocrine glands, including the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and gonads. It produces several hormones that stimulate or inhibit the production of hormones in other glands, maintaining a delicate balance of hormone levels in the body.
What are some common disorders of the pituitary gland?
+Common disorders of the pituitary gland include hypopituitarism, hyperpituitarism, pituitary tumors, and pituitary stalk compression. Symptoms can vary depending on the specific condition and the hormones affected.
How can I promote pituitary gland health?
+Ways to promote pituitary gland health include maintaining a healthy weight and diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, avoiding exposure to toxins and radiation, and getting regular medical check-ups and screenings.