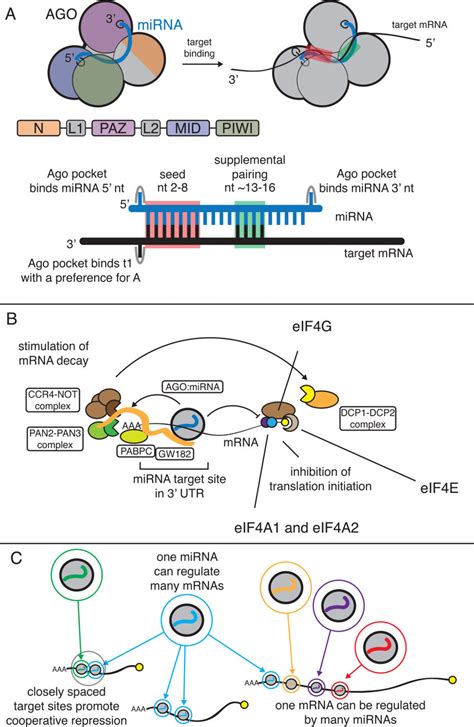
RNA regulation is a complex process that involves various molecules, including microRNAs (miRNAs). miRNAs are small, non-coding RNAs that play a crucial role in regulating gene expression. They have been found to be involved in numerous biological processes, including development, differentiation, growth, and metabolism. In this article, we will explore five ways miRNAs function in RNA regulation.
The Role of miRNAs in RNA Regulation
MicroRNAs are involved in the regulation of RNA expression by binding to complementary sequences on target messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. This binding can lead to the degradation of the mRNA or the inhibition of its translation into protein. miRNAs have been found to regulate various aspects of RNA biology, including RNA processing, transport, and translation.

1. miRNAs as Post-Transcriptional Regulators
One of the primary ways miRNAs function in RNA regulation is as post-transcriptional regulators. They bind to the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNAs, leading to the degradation of the mRNA or the inhibition of its translation. This binding is specific and is determined by the seed region of the miRNA, which is a 2-8 nucleotide sequence at the 5' end of the miRNA. The seed region is responsible for the recognition of the target mRNA.
How miRNAs Regulate mRNA Degradation
miRNAs can regulate mRNA degradation by binding to the 3' UTR of the target mRNA. This binding leads to the recruitment of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which is responsible for the degradation of the mRNA. The RISC complex contains the Argonaute protein, which is a key component of the miRNA-mediated RNA silencing pathway.
2. miRNAs as Epigenetic Regulators
miRNAs can also function as epigenetic regulators by influencing the expression of genes involved in epigenetic regulation. They can bind to the promoter regions of target genes, leading to the activation or repression of gene expression. miRNAs can also regulate the expression of epigenetic regulators, such as DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases.

3. miRNAs as Regulators of RNA Processing
miRNAs can regulate RNA processing by influencing the splicing, editing, and transport of RNAs. They can bind to the precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) and regulate its splicing, leading to the production of different isoforms of the mRNA. miRNAs can also regulate the editing of RNAs, such as the modification of adenosine to inosine.
How miRNAs Regulate RNA Splicing
miRNAs can regulate RNA splicing by binding to the pre-mRNA and influencing the activity of the splicing machinery. They can bind to the splice sites and regulate the recognition of the splice sites by the splicing machinery.
4. miRNAs as Regulators of RNA Transport
miRNAs can regulate RNA transport by influencing the movement of RNAs from one cellular compartment to another. They can bind to the RNA and regulate its transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.

5. miRNAs as Regulators of RNA Translation
miRNAs can regulate RNA translation by influencing the initiation and elongation of protein synthesis. They can bind to the mRNA and regulate its translation by influencing the activity of the translation machinery.
How miRNAs Regulate RNA Translation
miRNAs can regulate RNA translation by binding to the mRNA and influencing the recognition of the start codon by the translation machinery. They can also regulate the elongation of protein synthesis by influencing the activity of the translation machinery.
Conclusion
MicroRNAs play a crucial role in the regulation of RNA expression. They function as post-transcriptional regulators, epigenetic regulators, regulators of RNA processing, regulators of RNA transport, and regulators of RNA translation. The binding of miRNAs to target mRNAs can lead to the degradation of the mRNA or the inhibition of its translation. Understanding the mechanisms of miRNA-mediated RNA regulation can provide insights into the regulation of gene expression and the development of diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of microRNAs in RNA regulation?
+The primary function of microRNAs in RNA regulation is to bind to target mRNAs and regulate their expression by influencing their degradation or translation.
How do microRNAs regulate RNA processing?
+MicroRNAs can regulate RNA processing by influencing the splicing, editing, and transport of RNAs. They can bind to the precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) and regulate its splicing, leading to the production of different isoforms of the mRNA.
What is the role of microRNAs in epigenetic regulation?
+MicroRNAs can function as epigenetic regulators by influencing the expression of genes involved in epigenetic regulation. They can bind to the promoter regions of target genes, leading to the activation or repression of gene expression.