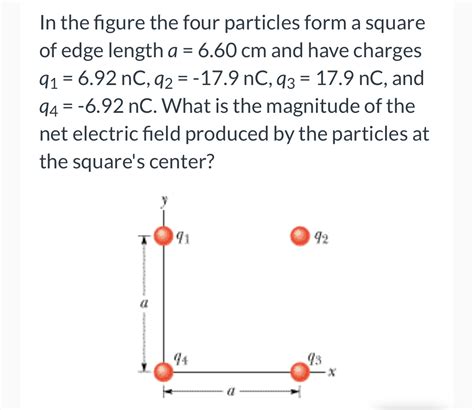
The behavior of particles at the smallest scales has always fascinated physicists and engineers. One intriguing phenomenon is the formation of a square by four particles. This may seem like a simple geometric arrangement, but the underlying physics is complex and multifaceted. In this article, we will delve into the physics behind the formation of a square by four particles, exploring the concepts that govern their behavior.

Introduction to Particle Interactions
When particles interact with each other, they exhibit complex behaviors that are influenced by various physical forces. These interactions can be attractive or repulsive, depending on the nature of the particles and the forces involved. In the context of four particles forming a square, we need to consider the types of interactions that govern their behavior.
At the atomic and subatomic level, particles interact through fundamental forces such as electromagnetism, weak nuclear force, and strong nuclear force. These forces dictate the behavior of particles in various physical systems, including solids, liquids, and gases. In the case of four particles forming a square, we can focus on the electromagnetic force, which is responsible for the interactions between charged particles.
Electromagnetic Interactions and Particle Arrangement
The electromagnetic force is a long-range force that acts between charged particles. When two particles with the same charge interact, they experience a repulsive force, while particles with opposite charges experience an attractive force. In the context of four particles forming a square, the arrangement of particles is influenced by the balance between attractive and repulsive forces.

Consider a scenario where four particles with the same charge are placed in close proximity. Initially, the particles will experience a repulsive force, causing them to move away from each other. However, as the particles move, they begin to interact with each other through attractive forces, which counterbalance the repulsive forces. This balance of forces leads to the formation of a stable arrangement, where the particles form a square.
Quantum Mechanics and Particle Behavior
The behavior of particles at the smallest scales is governed by the principles of quantum mechanics. According to the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, particles exhibit wave-like behavior, and their positions and momenta are uncertain. This uncertainty principle has significant implications for the behavior of particles in a square arrangement.

In a square arrangement, the particles exhibit a high degree of symmetry, which is influenced by the wave-like behavior of the particles. The particles' wave functions overlap, leading to the formation of a stable arrangement. This arrangement is characterized by a specific energy level, which is determined by the interactions between the particles.
Energy Minimization and Stable Arrangements
The formation of a square by four particles can be understood in terms of energy minimization. The particles arrange themselves in a way that minimizes their total energy, which is influenced by the interactions between the particles. This energy minimization principle is a fundamental concept in physics, governing the behavior of particles in various physical systems.

In the context of four particles forming a square, the energy minimization principle leads to the formation of a stable arrangement. The particles arrange themselves in a way that balances the attractive and repulsive forces, resulting in a stable energy level. This stable arrangement is characterized by a specific geometric configuration, which is influenced by the symmetry of the particles' wave functions.
Applications and Implications
The physics behind four particles forming a square has significant implications for various fields, including materials science, chemistry, and physics. Understanding the behavior of particles at the smallest scales is crucial for the development of new materials and technologies.

In materials science, the behavior of particles in a square arrangement can be used to design new materials with specific properties. For example, researchers can use the principles of energy minimization to design materials with high strength and low weight. In chemistry, the behavior of particles in a square arrangement can be used to understand the properties of molecules and their interactions.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the physics behind four particles forming a square is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that is governed by the principles of quantum mechanics and energy minimization. Understanding the behavior of particles at the smallest scales is crucial for the development of new materials and technologies.
As research continues to advance, we can expect to see new applications and implications of the physics behind four particles forming a square. By exploring the behavior of particles at the smallest scales, researchers can gain insights into the fundamental laws of physics and develop new technologies that transform our world.
We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this article. How do you think the physics behind four particles forming a square can be applied to real-world problems? Share your ideas and let's continue the conversation!
What is the primary force responsible for the interactions between particles in a square arrangement?
+The primary force responsible for the interactions between particles in a square arrangement is the electromagnetic force.
What principle governs the behavior of particles at the smallest scales?
+The behavior of particles at the smallest scales is governed by the principles of quantum mechanics.
What is the significance of energy minimization in the context of four particles forming a square?
+Energy minimization is significant in the context of four particles forming a square because it leads to the formation of a stable arrangement, which is characterized by a specific energy level.