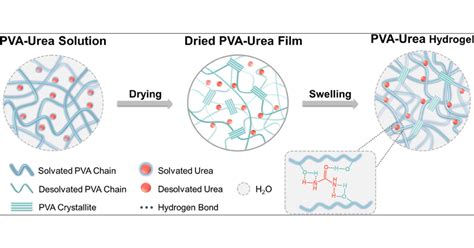
Hydrogen bonding is a crucial aspect of many biological and chemical processes, and ureas are no exception. Ureas, a class of organic compounds, have been found to exhibit unique hydrogen bonding properties that make them useful in various applications. In this article, we will delve into the world of ureas and explore their hydrogen bonding capacity, including its mechanisms, benefits, and applications.
Understanding Hydrogen Bonding in Ureas

Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. In the case of ureas, the hydrogen bonding capacity is primarily due to the presence of the carbonyl group (C=O) and the amino group (NH2). The carbonyl group acts as a hydrogen bond acceptor, while the amino group acts as a hydrogen bond donor.
Mechanisms of Hydrogen Bonding in Ureas
The mechanisms of hydrogen bonding in ureas involve the formation of a hydrogen bond between the carbonyl group and the amino group of adjacent urea molecules. This is facilitated by the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom of the amino group, which is attracted to the partial negative charge on the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group.
The strength of the hydrogen bond in ureas is influenced by several factors, including the distance between the molecules, the orientation of the molecules, and the presence of other functional groups. The hydrogen bond energy in ureas is typically in the range of 10-30 kJ/mol, which is relatively strong compared to other types of intermolecular forces.
Benefits of Ureas' Hydrogen Bonding Capacity

The hydrogen bonding capacity of ureas has several benefits, including:
- Improved solubility: The ability of ureas to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules enhances their solubility in aqueous solutions.
- Increased melting point: The strong intermolecular forces between urea molecules result in a higher melting point compared to other organic compounds.
- Enhanced stability: The hydrogen bonding capacity of ureas contributes to their stability and resistance to degradation.
- Biological activity: The ability of ureas to form hydrogen bonds with biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, is crucial for their biological activity.
Applications of Ureas' Hydrogen Bonding Capacity
The unique hydrogen bonding properties of ureas have led to their application in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Ureas are used as excipients in pharmaceutical formulations to enhance the solubility and stability of active ingredients.
- Agriculture: Ureas are used as fertilizers due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds with soil particles, enhancing their retention and availability to plants.
- Biotechnology: Ureas are used as denaturants in protein purification and as cryoprotectants in the preservation of biological samples.
Types of Ureas and Their Hydrogen Bonding Capacity

There are several types of ureas, each with its unique hydrogen bonding capacity. Some of the most common types of ureas include:
- Urea: The simplest type of urea, with a single carbonyl group and two amino groups.
- Biuret: A type of urea with two carbonyl groups and four amino groups.
- Triuret: A type of urea with three carbonyl groups and six amino groups.
Each type of urea has its unique hydrogen bonding capacity, which is influenced by the number and arrangement of the carbonyl and amino groups.
Factors Affecting Ureas' Hydrogen Bonding Capacity
Several factors can affect the hydrogen bonding capacity of ureas, including:
- pH: The pH of the solution can influence the ionization state of the amino and carbonyl groups, affecting the hydrogen bonding capacity.
- Temperature: The temperature of the solution can influence the strength and stability of the hydrogen bonds.
- Solvent: The type of solvent used can influence the hydrogen bonding capacity by affecting the dielectric constant and the ability of the solvent to form hydrogen bonds with the urea molecules.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the hydrogen bonding capacity of ureas is a unique property that has several benefits and applications. Understanding the mechanisms and factors that influence the hydrogen bonding capacity of ureas is crucial for the development of new applications and technologies.
Future research directions may include the exploration of new types of ureas with enhanced hydrogen bonding capacity, the development of new applications for ureas in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals, and the investigation of the role of ureas in biological systems.
What is hydrogen bonding in ureas?
+Hydrogen bonding in ureas refers to the intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
What are the benefits of ureas' hydrogen bonding capacity?
+The benefits of ureas' hydrogen bonding capacity include improved solubility, increased melting point, enhanced stability, and biological activity.
What are the applications of ureas' hydrogen bonding capacity?
+The applications of ureas' hydrogen bonding capacity include pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and biotechnology.