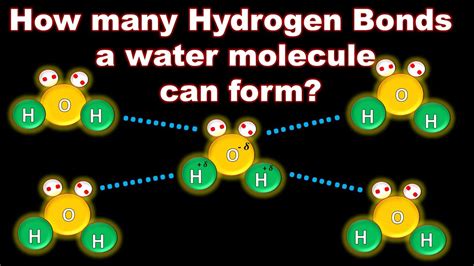
Water is one of the most essential molecules on Earth, and its unique properties make it crucial for life as we know it. One of the key features of water molecules is their ability to form hydrogen bonds, which play a vital role in many biological and chemical processes. But have you ever wondered how many hydrogen bonds one water molecule can form?

In this article, we'll delve into the world of hydrogen bonding and explore the fascinating properties of water molecules. We'll discuss the science behind hydrogen bonding, the factors that influence the number of hydrogen bonds a water molecule can form, and the significance of these bonds in various biological and chemical processes.
What are Hydrogen Bonds?
Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. These bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent bonds but play a crucial role in the structure and properties of many biological molecules, including DNA, proteins, and water.
In the case of water molecules, hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen atoms of one molecule and the oxygen atoms of another. This occurs because the oxygen atom in a water molecule has a slightly negative charge, while the hydrogen atoms have a slightly positive charge. This polarity allows the hydrogen atoms to be attracted to the oxygen atoms of neighboring molecules, forming a hydrogen bond.
Factors that Influence Hydrogen Bonding
Several factors influence the number of hydrogen bonds a water molecule can form, including:
- Temperature: Hydrogen bonding is more prevalent at lower temperatures, as the molecules have less kinetic energy and are more likely to form bonds.
- Pressure: Increased pressure can disrupt hydrogen bonds, reducing the number of bonds formed.
- Concentration: The concentration of water molecules can affect the number of hydrogen bonds formed, with more concentrated solutions typically having more bonds.
- pH: The pH of a solution can influence the number of hydrogen bonds formed, with acidic or basic conditions affecting the ionization of water molecules.
How Many Hydrogen Bonds Can One Water Molecule Form?
In ideal conditions, a single water molecule can form up to four hydrogen bonds with neighboring molecules. However, this number can vary depending on the factors mentioned above.
- Two hydrogen bonds can form between the hydrogen atoms of one water molecule and the oxygen atoms of two neighboring molecules.
- Two additional hydrogen bonds can form between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and the hydrogen atoms of two neighboring molecules.
This tetrahedral arrangement of hydrogen bonds is crucial for the unique properties of water, including its high boiling point, surface tension, and ability to dissolve a wide range of substances.

Significance of Hydrogen Bonds in Biological Processes
Hydrogen bonds play a vital role in many biological processes, including:
- Protein structure and function: Hydrogen bonds help stabilize the 3D structure of proteins and facilitate their interactions with other molecules.
- DNA structure and replication: Hydrogen bonds between DNA bases and the phosphate backbone are crucial for the stability and replication of DNA.
- Cell signaling and transport: Hydrogen bonds can facilitate the transport of molecules across cell membranes and play a role in cell signaling pathways.
Hydrogen Bonds in Chemical Processes
Hydrogen bonds also play a significant role in various chemical processes, including:
- Solubility: Hydrogen bonds can affect the solubility of substances in water, with some molecules forming hydrogen bonds with water molecules and increasing their solubility.
- Boiling point: Hydrogen bonds contribute to the high boiling point of water, as the bonds between molecules must be broken before the water can vaporize.
- Surface tension: Hydrogen bonds between water molecules at the surface of a solution can create a "skin" that affects the solution's surface tension.

Practical Applications of Hydrogen Bonds
Understanding hydrogen bonds has numerous practical applications, including:
- Designing new materials: Knowledge of hydrogen bonds can inform the design of new materials with specific properties, such as high strength or low surface energy.
- Developing new pharmaceuticals: Understanding the role of hydrogen bonds in protein-ligand interactions can aid in the development of new pharmaceuticals.
- Improving water treatment: Recognizing the importance of hydrogen bonds in water chemistry can lead to more efficient water treatment processes.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the ability of water molecules to form hydrogen bonds is a fascinating and complex phenomenon that plays a crucial role in many biological and chemical processes. Understanding the science behind hydrogen bonding and the factors that influence the number of bonds formed can have significant implications for various fields, from materials science to pharmaceuticals.
By exploring the intricacies of hydrogen bonding, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the unique properties of water and its importance in our daily lives.

Take Action
We hope this article has inspired you to learn more about the fascinating world of hydrogen bonding. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about the natural world, there's always more to discover. Take a moment to share this article with a friend or colleague, or explore other resources on this topic. Who knows what new discoveries await?
What is the significance of hydrogen bonds in biological processes?
+Hydrogen bonds play a vital role in many biological processes, including protein structure and function, DNA structure and replication, and cell signaling and transport. They help stabilize the 3D structure of proteins, facilitate interactions between molecules, and contribute to the stability and replication of DNA.
How do hydrogen bonds affect the solubility of substances in water?
+Hydrogen bonds can affect the solubility of substances in water by forming bonds between the substance and water molecules. This can increase the solubility of the substance, as the bonds between the substance and water molecules help to stabilize the substance in the solution.
What is the relationship between hydrogen bonds and the boiling point of water?
+Hydrogen bonds contribute to the high boiling point of water by forming bonds between water molecules. These bonds must be broken before the water can vaporize, which requires a significant amount of energy and results in a higher boiling point.