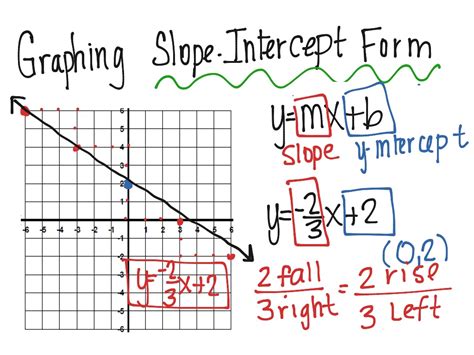
The slope-intercept form is one of the most widely used forms of linear equations, and graphing it can be a breeze with the right techniques. Mastering slope-intercept form graphing is essential for students, math enthusiasts, and professionals who deal with linear equations on a daily basis. In this article, we will explore five easy ways to master slope-intercept form graphing, along with practical examples and tips to help you become a pro.
Slope-intercept form is a linear equation that takes the form y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line and b represents the y-intercept. Understanding the concept of slope and y-intercept is crucial to graphing slope-intercept form equations. The slope of a line is a measure of how steep it is, while the y-intercept is the point where the line intersects the y-axis.

1. Understanding the Slope
The slope of a line is a critical component of slope-intercept form graphing. The slope represents the rate of change of the line, which can be positive, negative, or zero. A positive slope indicates that the line is rising from left to right, while a negative slope indicates that the line is falling from left to right. A zero slope indicates that the line is horizontal.
To calculate the slope, you can use the formula m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are two points on the line. Once you have the slope, you can use it to graph the line.

Tips for Calculating Slope
- Always use two points on the line to calculate the slope.
- Make sure the points are accurate to get an accurate slope.
- Use the formula m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) to calculate the slope.
2. Understanding the Y-Intercept
The y-intercept is the point where the line intersects the y-axis. It's an essential component of slope-intercept form graphing, as it helps you to determine the starting point of the line. The y-intercept can be positive, negative, or zero.
To find the y-intercept, you can look at the equation and identify the value of b. The y-intercept is the point (0, b) on the graph.

Tips for Finding Y-Intercept
- Identify the value of b in the equation y = mx + b.
- The y-intercept is the point (0, b) on the graph.
- Use the y-intercept to determine the starting point of the line.
3. Graphing Slope-Intercept Form Equations
Now that you understand the slope and y-intercept, it's time to graph slope-intercept form equations. To graph a slope-intercept form equation, follow these steps:
- Identify the slope and y-intercept from the equation.
- Plot the y-intercept on the graph.
- Use the slope to determine the direction of the line.
- Plot a second point on the line using the slope.
- Draw a line through the two points.

Tips for Graphing Slope-Intercept Form Equations
- Use a graph paper to graph slope-intercept form equations.
- Plot the y-intercept accurately to ensure the line is correct.
- Use the slope to determine the direction of the line.
4. Using X-Intercepts and Midpoints
X-intercepts and midpoints are additional tools that can help you graph slope-intercept form equations. The x-intercept is the point where the line intersects the x-axis, while the midpoint is the point halfway between two points on the line.
To find the x-intercept, set y = 0 in the equation and solve for x. To find the midpoint, use the formula (x1 + x2) / 2, (y1 + y2) / 2.

Tips for Using X-Intercepts and Midpoints
- Use x-intercepts to determine the point where the line intersects the x-axis.
- Use midpoints to find the point halfway between two points on the line.
5. Practicing with Examples
Practice is key to mastering slope-intercept form graphing. Here are a few examples to help you get started:
Example 1: Graph the equation y = 2x + 3.
Solution: Identify the slope (m = 2) and y-intercept (b = 3). Plot the y-intercept on the graph. Use the slope to determine the direction of the line. Plot a second point on the line using the slope. Draw a line through the two points.
Example 2: Graph the equation y = -x - 2.
Solution: Identify the slope (m = -1) and y-intercept (b = -2). Plot the y-intercept on the graph. Use the slope to determine the direction of the line. Plot a second point on the line using the slope. Draw a line through the two points.

Tips for Practicing with Examples
- Start with simple equations and gradually move to more complex ones.
- Practice graphing different types of slope-intercept form equations.
- Use online resources or graphing calculators to check your answers.
What is the slope-intercept form of a linear equation?
+The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line and b represents the y-intercept.
How do I calculate the slope of a line?
+To calculate the slope, use the formula m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are two points on the line.
What is the y-intercept of a line?
+The y-intercept is the point where the line intersects the y-axis. It's an essential component of slope-intercept form graphing, as it helps you to determine the starting point of the line.
By following these five easy ways to master slope-intercept form graphing, you'll become proficient in graphing linear equations in no time. Remember to practice regularly and use online resources or graphing calculators to check your answers. With time and practice, you'll become a pro at graphing slope-intercept form equations!