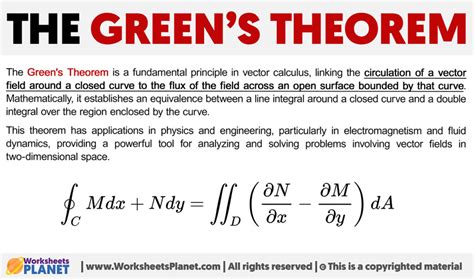
Green's Theorem is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in the field of calculus. It provides a powerful tool for evaluating line integrals and has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other fields. In this article, we will delve into the flux form of Green's Theorem, exploring its definition, significance, and practical applications.
The Flux Form of Green's Theorem
Green's Theorem comes in two forms: the circulation form and the flux form. While the circulation form deals with the line integral of a vector field around a closed curve, the flux form concerns itself with the line integral of a vector field across a surface bounded by a closed curve. The flux form of Green's Theorem states that the line integral of a vector field across a surface can be converted into a double integral over the region bounded by the surface.
Mathematical Formulation

Mathematically, the flux form of Green's Theorem can be expressed as:
∮_(∂D) F · dr = ∬_D (∂Q/∂x - ∂P/∂y) dA
where:
- F = (P, Q) is a vector field
- ∂D is the boundary of the region D
- F · dr is the dot product of the vector field F and the infinitesimal displacement vector dr
- ∂Q/∂x - ∂P/∂y is the curl of the vector field F
Significance of the Flux Form
The flux form of Green's Theorem has far-reaching implications in various fields. In physics, it helps calculate the flux of a vector field across a surface, which is essential in understanding concepts like electric and magnetic fields. In engineering, it is used to determine the flow rate of fluids and gases across a surface. Additionally, the flux form of Green's Theorem is instrumental in solving partial differential equations (PDEs) and has applications in computer graphics, image processing, and computational fluid dynamics.
Applications of the Flux Form

The flux form of Green's Theorem has numerous practical applications in various fields. Some of the notable applications include:
- Electric and Magnetic Fields: The flux form of Green's Theorem helps calculate the electric flux across a surface, which is crucial in understanding electromagnetic phenomena.
- Fluid Dynamics: The theorem is used to calculate the flow rate of fluids and gases across a surface, which is essential in understanding fluid dynamics.
- Computer Graphics: The flux form of Green's Theorem is used in computer graphics to simulate the flow of fluids and gases.
- Image Processing: The theorem is used in image processing to detect edges and boundaries in images.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics: The flux form of Green's Theorem is used to solve PDEs in computational fluid dynamics.
Steps to Apply the Flux Form
To apply the flux form of Green's Theorem, follow these steps:
- Define the vector field F = (P, Q) and the region D.
- Calculate the curl of the vector field F, i.e., ∂Q/∂x - ∂P/∂y.
- Evaluate the double integral of the curl over the region D.
- The result will give you the flux of the vector field across the surface.
Examples and Case Studies

Let's consider a few examples to illustrate the application of the flux form of Green's Theorem.
- Example 1: Calculate the electric flux across a surface using the flux form of Green's Theorem.
- Example 2: Use the theorem to determine the flow rate of a fluid across a surface.
- Case Study: Apply the flux form of Green's Theorem to simulate the flow of a gas across a surface.
Common Misconceptions
There are several common misconceptions associated with the flux form of Green's Theorem. Some of these include:
- Misconception 1: The flux form of Green's Theorem only applies to electric and magnetic fields.
- Misconception 2: The theorem is only used in physics and engineering.
In reality, the flux form of Green's Theorem has a wide range of applications across various fields.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the flux form of Green's Theorem is a powerful tool for evaluating line integrals and has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other fields. Understanding the theorem and its applications can help you solve complex problems and make informed decisions.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with the flux form of Green's Theorem in the comments section below. If you have any questions or need further clarification, please don't hesitate to ask.
FAQ Section
What is the flux form of Green's Theorem?
+The flux form of Green's Theorem is a mathematical statement that relates the line integral of a vector field across a surface to the double integral of the curl of the vector field over the region bounded by the surface.
What are the applications of the flux form of Green's Theorem?
+The flux form of Green's Theorem has numerous applications in physics, engineering, computer graphics, image processing, and computational fluid dynamics.
How do I apply the flux form of Green's Theorem?
+To apply the flux form of Green's Theorem, define the vector field F = (P, Q) and the region D, calculate the curl of the vector field F, and evaluate the double integral of the curl over the region D.