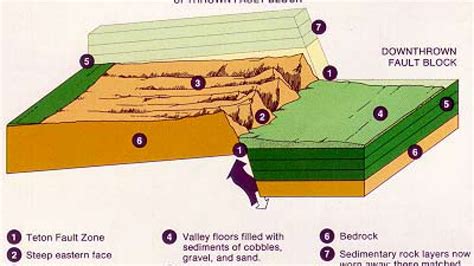
The Earth's surface is dynamic and constantly changing, with tectonic plates moving beneath our feet. One of the most striking features of this ever-changing landscape is the formation of block mountains, also known as fault-block mountains. These towering ranges are created when large blocks of the Earth's crust are pushed up or pulled down along fault lines, resulting in the formation of mountains. In this article, we will explore the process of block mountain formation, the characteristics of these mountains, and some examples of block mountain ranges around the world.

What are Block Mountains?
Block mountains are formed when large blocks of the Earth's crust are pushed up or pulled down along fault lines. Fault lines are cracks or fractures in the Earth's crust where tectonic plates meet and move past each other. When the movement along these fault lines is horizontal, it can cause the blocks of crust on either side of the fault to move up or down, resulting in the formation of mountains.
Block mountains can be formed through two main processes: normal faulting and reverse faulting. Normal faulting occurs when the blocks of crust on either side of the fault move apart, causing the block on one side to drop down and the block on the other side to rise up. Reverse faulting occurs when the blocks of crust on either side of the fault are pushed together, causing the block on one side to be pushed up and the block on the other side to be pulled down.
Characteristics of Block Mountains
Block mountains have several distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of mountains. Some of the key characteristics of block mountains include:
- Steep slopes: Block mountains tend to have steep slopes, which are formed as a result of the rapid uplift of the blocks of crust.
- Flat tops: Many block mountains have flat or gently sloping tops, which are formed as a result of the block of crust being pushed up or pulled down along the fault line.
- Linear shape: Block mountains often have a linear shape, with the range running parallel to the fault line.
- Lack of folding: Unlike fold mountains, block mountains are not formed through the folding of rocks. Instead, they are formed through the movement of large blocks of crust along fault lines.

Examples of Block Mountain Ranges
There are several examples of block mountain ranges around the world. Some of the most notable include:
- The Sierra Nevada mountain range in California, USA: This range was formed as a result of the movement of the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate along the San Andreas Fault.
- The Jura Mountains in Europe: This range was formed as a result of the movement of the Eurasian Plate and the African Plate along the Rhine Fault.
- The Drakensberg Mountains in South Africa: This range was formed as a result of the movement of the African Plate and the Antarctic Plate along the Drakensberg Fault.
- The mountain ranges of the Basin and Range Province in the western United States: This region is characterized by numerous block mountain ranges, including the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada.

The Process of Block Mountain Formation
The process of block mountain formation is complex and involves the movement of tectonic plates and the resulting deformation of the Earth's crust. Here is a step-by-step explanation of the process:
- Tectonic plate movement: The movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface causes stress to build up in the Earth's crust.
- Faulting: When the stress becomes too great, the Earth's crust breaks along a fault line, resulting in the formation of a fault.
- Block movement: As the tectonic plates continue to move, the blocks of crust on either side of the fault line move up or down, resulting in the formation of mountains.
- Uplift: The block of crust on one side of the fault line is pushed up, resulting in the formation of a mountain range.
- Erosion: Over time, the mountain range is shaped by erosion, which wears away the rocks and creates valleys and other features.

Benefits of Block Mountains
Block mountains provide numerous benefits to the environment and human populations. Some of the key benefits include:
- Habitat creation: Block mountains provide a unique habitat for a wide range of plant and animal species.
- Water sources: Many block mountain ranges are the source of rivers and streams, which provide water for human populations and ecosystems.
- Mineral resources: Block mountains are often rich in mineral resources, such as copper, gold, and silver.
- Tourism: Block mountains are popular tourist destinations, providing opportunities for hiking, skiing, and other outdoor activities.

Challenges and Risks Associated with Block Mountains
While block mountains provide numerous benefits, they also pose several challenges and risks. Some of the key challenges and risks include:
- Earthquakes: Block mountains are often located in seismically active regions, which can pose a risk to human populations and infrastructure.
- Landslides: The steep slopes of block mountains can be prone to landslides, which can be triggered by heavy rainfall or earthquakes.
- Erosion: The rocks that make up block mountains are often prone to erosion, which can lead to the loss of soil and rocks.
- Human settlement: The steep slopes of block mountains can make it difficult to build and settle in these regions.

Conclusion
Block mountains are a unique and fascinating feature of the Earth's landscape. Formed through the movement of tectonic plates and the resulting deformation of the Earth's crust, these mountains provide numerous benefits to the environment and human populations. However, they also pose several challenges and risks, including earthquakes, landslides, and erosion. By understanding the process of block mountain formation and the characteristics of these mountains, we can better appreciate the beauty and complexity of the Earth's landscape.

Now that you've read this article, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with block mountains. Have you ever visited a block mountain range? What did you think of the scenery and geology? Share your comments below!
What are block mountains?
+Block mountains are formed when large blocks of the Earth's crust are pushed up or pulled down along fault lines.
How are block mountains formed?
+Block mountains are formed through the movement of tectonic plates and the resulting deformation of the Earth's crust.
What are some examples of block mountain ranges?
+Some examples of block mountain ranges include the Sierra Nevada mountain range in California, USA, the Jura Mountains in Europe, and the Drakensberg Mountains in South Africa.