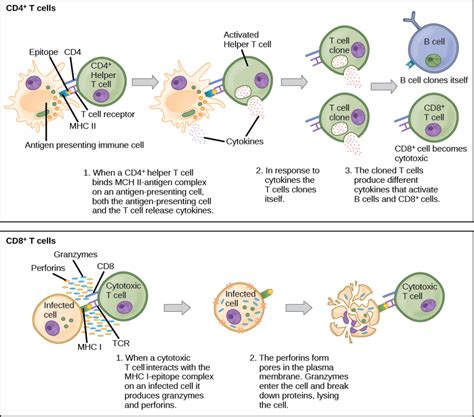
The immune system is a complex and fascinating network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. One of the key players in this system is the CD4 cell, a type of T cell that plays a central role in the immune response. In this article, we will explore the process of CD4 cell activation and cloning, and how these cells form a crucial part of our immune defense.

What are CD4 Cells?
CD4 cells, also known as T helper cells, are a type of T lymphocyte that expresses the CD4 protein on their surface. These cells play a crucial role in the immune response by helping to activate other immune cells, such as B cells and cytotoxic T cells, to fight infections. CD4 cells are named for the CD4 protein, which is a receptor that recognizes and binds to specific molecules on the surface of other cells.
How are CD4 Cells Activated?
CD4 cells are activated when they encounter specific antigens, such as proteins or sugars, on the surface of other cells. This encounter triggers a signaling cascade that ultimately leads to the activation of the CD4 cell. Once activated, CD4 cells undergo a process called clonal expansion, where they rapidly proliferate to form a large population of identical cells, known as a clone.
5 Ways Activated CD4 Cells Form a Clone
There are several ways in which activated CD4 cells can form a clone, including:
1. Cell Division
One of the primary ways that activated CD4 cells form a clone is through cell division. When a CD4 cell encounters an antigen, it becomes activated and begins to divide rapidly. This process is mediated by the production of cytokines, such as interleukin-2 (IL-2), which stimulate cell proliferation.
2. Differentiation
Activated CD4 cells can also differentiate into different subtypes, such as Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells, each with distinct functions. This differentiation process is crucial for the development of an effective immune response, as it allows the immune system to tailor its response to specific types of infections.
3. Cytokine Signaling
Cytokines play a crucial role in the activation and expansion of CD4 cells. Activated CD4 cells produce cytokines, such as IL-2, IL-4, and IL-12, which stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of other immune cells.
4. Antigen Presentation
Activated CD4 cells can also present antigens to other immune cells, such as B cells and cytotoxic T cells. This process, known as antigen presentation, is crucial for the activation of these cells and the development of an effective immune response.
5. Memory Cell Formation
Finally, activated CD4 cells can form memory cells, which are long-lived cells that remember specific antigens and can rapidly respond to future infections. This process is crucial for the development of long-term immunity and the prevention of future infections.

Benefits of CD4 Cell Cloning
The cloning of CD4 cells has several benefits, including:
- Rapid Expansion: Cloning allows for the rapid expansion of CD4 cells, which is crucial for the development of an effective immune response.
- Improved Immune Function: Cloning also improves immune function by allowing CD4 cells to differentiate into different subtypes, each with distinct functions.
- Long-term Immunity: Cloning also leads to the formation of memory cells, which are long-lived cells that remember specific antigens and can rapidly respond to future infections.
Challenges and Future Directions
While CD4 cell cloning is a crucial part of the immune response, there are several challenges and future directions that researchers are exploring, including:
- Understanding the mechanisms of CD4 cell activation and cloning: Further research is needed to understand the mechanisms of CD4 cell activation and cloning, and how these processes can be manipulated to improve immune function.
- Developing new treatments for immune-related diseases: Researchers are also exploring the development of new treatments for immune-related diseases, such as HIV and cancer, which involve the manipulation of CD4 cells.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the cloning of CD4 cells is a crucial part of the immune response, and has several benefits, including rapid expansion, improved immune function, and long-term immunity. However, there are also challenges and future directions that researchers are exploring, including understanding the mechanisms of CD4 cell activation and cloning, and developing new treatments for immune-related diseases.
Share Your Thoughts
We would love to hear your thoughts on CD4 cell cloning and its role in the immune response. Please share your comments and questions below, and don't forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues.
What is the main function of CD4 cells?
+The main function of CD4 cells is to help activate other immune cells, such as B cells and cytotoxic T cells, to fight infections.
How do CD4 cells become activated?
+CD4 cells become activated when they encounter specific antigens, such as proteins or sugars, on the surface of other cells.
What is the role of cytokines in CD4 cell activation?
+Cytokines, such as IL-2, IL-4, and IL-12, play a crucial role in the activation and expansion of CD4 cells.