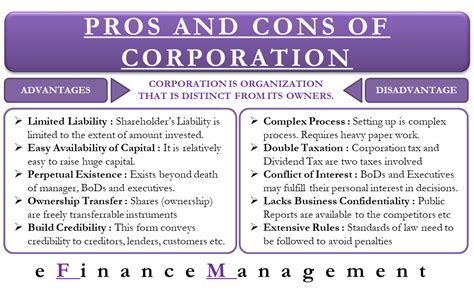
As businesses continue to evolve and grow, they often consider various forms of organization to suit their needs. One popular option is the corporate form of organization, which offers several benefits, including limited liability, tax advantages, and increased capital. However, like any business structure, it also has its drawbacks. In this article, we will delve into the five significant drawbacks of the corporate form of organization.
Double Taxation

One of the most significant drawbacks of the corporate form of organization is double taxation. In a corporation, the company is taxed on its profits, and then the shareholders are taxed again on the dividends they receive. This results in a higher overall tax burden, which can be detrimental to the business and its shareholders. This double taxation can discourage investors and limit the company's ability to raise capital.
Separation of Ownership and Control

In a corporation, ownership is separate from control. Shareholders own the company, but they do not directly control its operations. Instead, a board of directors and management team are responsible for making decisions and overseeing the business. This separation of ownership and control can lead to conflicts of interest and make it difficult for shareholders to have a direct say in the company's direction.
High Formation and Maintenance Costs

Forming and maintaining a corporation can be expensive. The cost of incorporation, including filing fees, attorney fees, and other expenses, can be substantial. Additionally, corporations are subject to ongoing compliance costs, such as annual reports, taxes, and regulatory fees. These costs can be a burden for small businesses or startups with limited resources.
Initial Public Offering (IPO) Costs
If a corporation decides to go public, the costs associated with an initial public offering (IPO) can be significant. The costs of preparing for an IPO, including underwriting fees, accounting fees, and marketing expenses, can range from 5% to 15% of the total offering.
Limited Flexibility

Corporations are subject to strict regulations and formalities, which can limit their flexibility. For example, corporations must hold annual meetings, maintain a board of directors, and follow specific procedures for decision-making. These formalities can make it difficult for corporations to respond quickly to changing market conditions or make rapid decisions.
Public Scrutiny and Disclosure

As a public entity, corporations are subject to public scrutiny and disclosure requirements. This can be a drawback for businesses that prefer to maintain their operations and financial information private. Publicly traded corporations must disclose financial information, management decisions, and other sensitive data, which can be a burden and create potential risks.
In conclusion, while the corporate form of organization offers several benefits, it also has significant drawbacks. Double taxation, separation of ownership and control, high formation and maintenance costs, limited flexibility, and public scrutiny and disclosure requirements are all potential drawbacks that businesses should carefully consider before choosing this form of organization.
If you have any thoughts or experiences with the corporate form of organization, we encourage you to share them with us in the comments below.
What are the main drawbacks of the corporate form of organization?
+The main drawbacks of the corporate form of organization include double taxation, separation of ownership and control, high formation and maintenance costs, limited flexibility, and public scrutiny and disclosure requirements.
How does double taxation affect corporations?
+Double taxation occurs when a corporation is taxed on its profits, and then the shareholders are taxed again on the dividends they receive. This results in a higher overall tax burden, which can be detrimental to the business and its shareholders.
What are the costs associated with forming and maintaining a corporation?
+The costs associated with forming and maintaining a corporation include filing fees, attorney fees, annual reports, taxes, and regulatory fees. These costs can be a burden for small businesses or startups with limited resources.